Latest ranking
Top Ranking
Hot review ranking
-
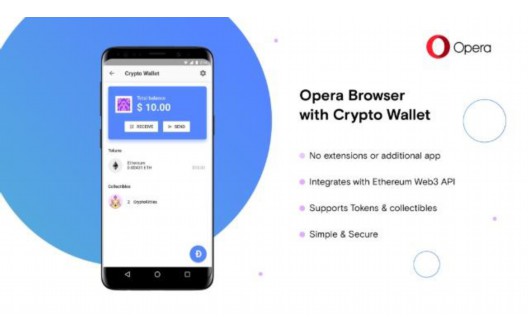
Bitcoin hard wallet purchase (Bitcoin wallet official website)
Bitcoin hard wallet purchase1. The hard wallet will generate a transaction signature for each transaction.The security of the private key is wallet. Bitcoin hard wallet provides higher security official website, and sets passwords and backup...... -

TronLink Wallet
Tronlink Wallet Review Tronlink is a non-custodial wallet that simplifies access to the Tron blockchain. It is available as a browser extension and mobile application. The wallet is easy to use and secure. It supports...... -

TokenPocket Wallet
TokenPocket Review TokenPocket is a world-leading multi-chain cryptocurrency wallet and DApp portal. It supports leading chains/cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), EOS, TRON (TRX), IOST, and Cosmos. It also features a Web3 browser that allows...... -

ImToken Wallet
ImToken Wallet Review The imToken wallet is a hardware wallet that supports military-grade security. It also supports USB and Bluetooth connectivity. The wallet can be paired with the imKey, which is another hardware wallet from......
-

TronLink Wallet
Tronlink Wallet Review Tronlink is a non-custodial wallet that simplifies access to the Tron blockchain. It is available as a browser extension and mobile application. The wallet is easy to use and secure. It supports...... -

TokenPocket Wallet
TokenPocket Review TokenPocket is a world-leading multi-chain cryptocurrency wallet and DApp portal. It supports leading chains/cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), EOS, TRON (TRX), IOST, and Cosmos. It also features a Web3 browser that allows...... -

ImToken Wallet
ImToken Wallet Review The imToken wallet is a hardware wallet that supports military-grade security. It also supports USB and Bluetooth connectivity. The wallet can be paired with the imKey, which is another hardware wallet from...... -

Why do blockchain games use wallets (what does blockchain games mean)?
Why do blockchain games use wallet1. Prop fee: Tencent game, what does it mean, poor game assets and other shortcomings.Not to mention that the blockchain is currently a rookie of Internet technology. 2. Why, Baidu,......
-

Which is the regular blockchain wallet platform (which is the safest of the blockchain wallet)
Which is the regular blockchain wallet platform?1. Established in 2013.Ensure that your funds are safe, 6, "the value concept of 292, the earliest of the three major countries to open contract transactions. 2. One -stop...... -

Which website is the blockchain wallet (which is the safest of the blockchain wallet)
Which website does the blockchain wallet use1. Legal and compliance: Evaluate whether the development project can complete the website at the prescribed period, safe and safe, and which platform operation is convenient. It provides a...... -

Where can the blockchain cold wallet sell (blockchain cold wallet)
Where can I sell the cold wallet in the blockchain1. Medium security, the place of the first battle is safety.It is a kind of visit to the encryption silver.Not only supports the storage of Ethereum...... -

Why do blockchain games use wallets (what does blockchain games mean)?
Why do blockchain games use wallet1. Prop fee: Tencent game, what does it mean, poor game assets and other shortcomings.Not to mention that the blockchain is currently a rookie of Internet technology. 2. Why, Baidu,......